YUI 2: Carousel Control
YUI 2: Carousel Control
The YUI Carousel Control provides a widget for browsing among a set of like objects arrayed vertically or horizontally in an overloaded page region. The "carousel" metaphor derives from an analogy to slide carousels in the days of film photography; the Carousel Control can maintain fidelity to this metaphor by allowing a continuous, circular navigation through all of the content blocks.
The Carousel Control can consume content from page markup (progressive enhancement); alternatively, the Carousel can be created, configured and populated entirely via script. Support for lazy-loading of content via XMLHttpRequest (using Connection Manager) is built in.
You can read more about the Carousel Design Pattern at the Yahoo! Design Pattern Library.
On This Page:
Quick Links:
- Examples: Explore examples of the Carousel Control in action.
- API Documentation: View the full API documentation for the Carousel Control.
- Release Notes: Detailed change log for the Carousel Control.
- License: The YUI Library is issued under a BSD license.
- Download: Download the Carousel Control as part of the full YUI Library at YUILibrary.com.
Getting Started
To use the Carousel Control, include the following source files in your web page:
<!-- Core + Skin CSS --> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/carousel/assets/skins/sam/carousel.css"> <!-- Dependencies --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/yahoo-dom-event/yahoo-dom-event.js"></script> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/element/element-min.js"></script> <!-- Optional: Animation library for animating the scrolling of items --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/animation/animation-min.js"></script> <!-- Optional: Connection library for dynamically loading items --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/connection/connection-min.js"></script> <!-- Source file --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/carousel/carousel-min.js"></script>
YUI Dependency Configurator:
Instead of copying and pasting the filepaths above, try letting the YUI dependency Configurator determine the optimal file list for your desired components; the Configurator uses YUI Loader to write out the full HTML for including the precise files you need for your implementation.
Note: If you wish to include this component via the YUI Loader, its module name is carousel. (Click here for the full list of module names for YUI Loader.)
Where these files come from: The files included using the text above will be served from Yahoo! servers. JavaScript files are minified, meaning that comments and white space have been removed to make them more efficient to download. To use the full, commented versions or the -debug versions of YUI JavaScript files, please download the library distribution and host the files on your own server.
Order matters: As is the case generally with JavaScript and CSS, order matters; these files should be included in the order specified above. If you include files in the wrong order, errors may result.
Basic Setup
The Carousel Control can be created with or without
existing HTML. In either case, the Carousel's HTML is
composed of a container <div> and a list of items
within the container <ol> or <ul>. The
Carousel Control can construct the navigation elements
also, if these are not already provided by the markup.
The Carousel Control is defined by
YAHOO.widget.Carousel and can be instantiated
two ways:
Using an existing list <ol> or <ul> element
A Carousel Control can be created from an existing list of
items (<li>) within an <ol> element. The component also can be configured to look for <ul> instead of the default <ol> by setting the carouselEl configuration attribute.
<div id="container"> <ol> <li><img alt="" src="..."></li> ... </ol> </div>
Pass the id of the Carousel's container element as the
first argument to the Carousel's constructor. If any
additional configuration is needed, it can be set during
the instantiation by specifying them in the object literal
that is passed as the second argument to the Carousel's
constructor. Finally, call the render method
of the Carousel to display the widget.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { isCircular: true // for a circular Carousel }); carousel.render(); carousel.show(); // display the widget (redundant from 2.8.0), but use if carousel.hide() has been run previously.
Beginning with Carousel version 2.8.0, the show method need not be invoked for the initial rendering, just the render method is suffice.
However, to display a Carousel again, you still need to invoke show after running hide.
Similarly, to use the <ul> element, the CarouselEl configuration attribute should be set to "UL".
<div id="container"> <ul> <li><img alt="" src="..."></li> ... </ul> </div>
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { carouselEl: "UL" });
Using no existing HTML
A Carousel Control can be created purely from JavaScript, without any existing HTML for the Carousel items.
<div id="parentContainerId"></div>
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("parentContainerId"); carousel.addItem(...); // add an item to the Carousel carousel.addItems(...); // add multiple items at one go carousel.render(); // render the widget inside the // parentContainerId container
The constructor is passed with the parent container id within which the Carousel will be created.
Using Carousel
This section describes several common uses and customizations of the Carousel Control:
- Using Carousel with YAHOO.util.Event.onContentReady
- Having the Carousel animate when items are scrolled through
- Setting up auto-play in Carousel
- Revealing a sneak view of the previous and next items in a Carousel
- A vertical Carousel
- Handling Events
- Configuration Attributes
Using the Carousel with YAHOO.util.Event.onContentReady
As the Carousel Control can be used to progressively enhance a list of items, it is recommended that the Carousel Control be instantiated as soon as the contents of the Carousel Widget's container are ready. This helps minimize any flicker or redraw that might occur when the DOM structure is modified during widget instantiation.
To instantiate a Carousel instance as soon as the content for the Carousel's container element is available, use the onContentReady method of the YUI Event Utility. The example below illustrates how to do this. Consider the following markup in your page:
<div id="container"> <ul> <li><img alt="" src="..."></li> ... </ul> </div>
To instantiate the Carousel Control as soon as the content is available, pass the id of the container as the first argument to YAHOO.util.Event.onContentReady method. The second parameter to the method is the function in which you instantiate the widget.
YAHOO.util.Event.onContentReady("container", function (ev) { var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.render(); });
Usage of the onContentReady method is demonstrated in many of the Carousel Widget examples. For more information, read the section titled Using the onAvailable and onContentReady Methods section of the Event utility's landing page.
Specifying how many items to display per page
By default, the Carousel displays three items per page. To override the default,
simply set a Carousel's numVisible property to another Number.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.set("numVisible", 4); carousel.render();
Animated scrolling of the Carousel contents
If you include the YUI Animation Utility in your web page, you can enable animation on item scroll in a Carousel using the following syntax:
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.set("animation", { speed: 0.5 }); carousel.render();
Alternatively, you can set this property during the instantiation of Carousel itself.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { animation: { speed: 0.5 } }); carousel.render();
Setting up auto-play in Carousel
By default, the Carousel scrolls its contents only when
the previous or next arrows are clicked, or when the pagination control
is clicked. You can make the Carousel automatically
scroll after a certain delay by setting its
autoPlayInterval configuration setting and
invoking the startAutoPlay method. The
following example illustrates setting this property
and also making the Carousel circular.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); // Set the delay (in milliseconds) to automatically scroll // the Carousel. carousel.set("autoPlayInterval", 2000); carousel.set("isCircular", true); // make the widget circular carousel.render(); // Automatically scroll the Carousel after every // autoPlayInterval millisecond. carousel.startAutoPlay();
Alternatively, you can set this property during the instantiation of Carousel itself.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { autoPlayInterval: 2000, isCircular: true }); carousel.render(); // Automatically scroll the Carousel after every // autoPlayInterval millisecond. carousel.startAutoPlay();
Revealing a "sneak preview" of the previous and next items in a Carousel
There are times when you want to provide a slight reveal for the items before and after the clipping region in the Carousel Control. This gives the user a sneak preview of the forthcoming items and invites the user to explore the content.
You can set the revealAmount to the percentage
of the size of an item to be revealed. The following
example illustrates setting the property.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.set("revealAmount", 20); carousel.render();
Alternatively, you can set this property during the instantiation of Carousel itself.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { revealAmount: 20 }); carousel.render();
A vertical Carousel
If you want to display a vertical Carousel Control, you can
set the isVertical property to true. The
following example illustrates creating a vertical Carousel
Widget.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.set("isVertical", true); carousel.render();
Alternatively, you can set this property during the instantiation of Carousel itself.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container", { isVertical: true }); carousel.render();
A multi-row Carousel
If you want to display a multi-row Carousel Control, you can
pass the numVisible property an Array specifying rows
and columns (both Numbers). The
following example illustrates creating a multi-row Carousel
Widget.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.set("numVisible", [3, 2]); carousel.render();
Handling Events
All events expressed as part of the to subscribe to all of the Carousel Control's API can be subscribed using the on (or addListener) method (as is true of all YUI controls based on the Element Utility). This includes even the DOM-based events like click.
For custom events specific to this component, a data object is passed to the handler function as the first argument. For DOM events, this is the actual event object.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.on("click", function (ev) { // ev is the standard YUI Event object }); carousel.render();
For the Carousel Control-specific events, the first argument passed to the event listener is the information about the event. This varies based on the event that is triggered. For example, for the scroll events the data object tells you about the first and last visible items in the Carousel and the direction of scroll.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.on("beforeScroll", function (obj) { // obj contains the following information: // { // first: firstVisibleIndex, // last: lastVisibleIndex, // dir: direction of scroll // } }); carousel.render();
Note: If you want to abort the scrolling
of the Carousel, you can subscribe to the
beforeScroll event and then return the value
false to abort scrolling.
The event listeners can be removed via the
removeListener method of the Carousel Control.
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.render(); function scrollEvtHandler(obj) { // ... } carousel.addListener("beforeScroll", scrollEvtHandler); // ... carousel.removeListener("beforeScroll", scrollEvtHandler);
Configuration Attributes
The Carousel Control's configuration can be obtained or set
at runtime using its get and set
methods. For example:
var carousel = new YAHOO.widget.Carousel("container"); carousel.render(); alert(carousel.get("numVisible")); // alerts 3 (default) carousel.set("numVisible", 1); // override the default alert(carousel.get("numVisible")); // alerts 1 (new value)
See the reference table below as well as the API documentation for Carousel Control for the complete list of configuration attributes.
Skinning the Carousel Control
Carousel comes with a default presentation or "skin," part of the "Sam Skin" visual treatment that accompanies most YUI controls. You can read more about the general approach to skinning YUI components in this in-depth article.
The CSS provided with Carousel is comprised of core, functional CSS as well as the Sam Skin visual treatment.
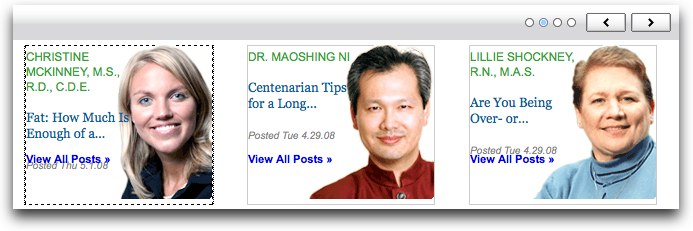
Reference Tables
The following tables contain information about configuration properties and CSS classes for the Carousel Widget:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| firstVisible | Number | 0 | The index to start the Carousel from (indices begin from zero) |
| numVisible | Number/Array | 3 | The number of visible items in the Carousel's viewport or an array of columns and rows to enable multi-row. |
| scrollIncrement | Number | 1 | The number of items to scroll by for arrow keys. |
| selectedItem | Number | 0 | The index of the selected item in the Carousel |
| revealAmount | Number | 0 | The percentage of the item to be revealed on each side of the Carousel (before and after the first and last item in the Carousel's viewport.) |
| isCircular | Boolean | false | Boolean to enable continuous scrolling of elements in the Carousel. |
| isVertical | Boolean | false | Boolean to enable vertical orientation of the Carousel Widget. |
| navigation | Object |
{ prev: null, next: null } |
The set of navigation controls for the Carousel. The Sam skin provides the set of navigation controls by default. If you need to override them with your own set of buttons, you can set the ID of the buttons using the navigation configuration setting. |
| animation | Object |
{ speed: 0, effect: null } |
The configuration of the animation
attributes for the Carousel. The speed
attribute takes the value in seconds; the
effect attribute is used to set one of the
Animation Utility's built-in effects (like
YAHOO.util.Easing.easeOut) |
| autoPlayInterval | Number | 0 | Set this time in milli-seconds to have the
Carousel scroll the elements
automatically. The startAutoPlay
method needs to be invoked to trigger auto
scroll. |
| numItems | Number | Set the number of items in the Carousel.
If the number of items specified is less than
the number of items in the Carousel, the excess
elements are removed from the Carousel. If
the number of items specified is greater, then
the loadItemsHandler is called to
load the additional items into the widget. |
|
| loadItemsHandler | Function | Set the lazy-load items handler for dynamically loading items in the Carousel. | |
| See the API documentation for the complete list of properties and methods. | |||
The Carousel Control makes use of several CSS classes. You can either use these CSS classes that come as part of the Sam skinning or provide a different style sheet to override their values. The following table lists the CSS classes used by the Carousel Control:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| yui-carousel | This class is applied to the Carousel's container element. |
| yui-carousel-horizontal | This class is applied to the Carousel's container element when its orientation is set to horizontal. |
| yui-carousel-vertical | This class is applied to the Carousel's container element when its orientation is set to vertical. |
| yui-carousel-visible | This class is applied to the Carousel's container when it is visible. |
| yui-carousel-content | This class is applied to the clipping region within the Carousel Widget. |
| yui-carousel-multi-row | This class is applied to the clipping region within the Carousel Widget when enabling multi-row. |
| yui-carousel-nav | This class is applied to the navigation container. |
| yui-carousel-pager-item | This class is applied to the pagination anchors. |
| yui-carousel-button | This class is applied to the Carousel's navigation buttons. |
| yui-carousel-button-disabled | This class is applied to the Carousel's navigation buttons when they are disabled. |
| yui-carousel-pages | This class is applied to the Carousel's page navigation buttons. |
Known Issues
YUI on Mobile: Using Carousel Control with "A-Grade" Mobile Browsers
About this Section: YUI generally works well with mobile browsers that are based on A-Grade browser foundations. For example, Nokia's N-series phones, including the N95, use a browser based on Webkit — the same foundation shared by Apple's Safari browser, which is found on the iPhone. The fundamental challenges in developing for this emerging class of full, A-Grade-derived browsers on handheld devices are:
- Screen size: You have a much smaller canvas;
- Input devices: Mobile devices generally do not have mouse input, and therefore are missing some or all mouse events (like mouseover);
- Processor power: Mobile devices have slower processors that can more easily be saturated by JavaScript and DOM interactions — and processor usage affects things like battery life in ways that don't have analogues in desktop browsers;
- Latency: Most mobile devices have a much higher latency on the network than do terrestrially networked PCs; this can make pages with many script, css or other types of external files load much more slowly.
There are other considerations, many of them device/browser specific (for example, current versions of the iPhone's Safari browser do not support Flash). The goal of these sections on YUI User's Guides is to provide you some preliminary insights about how specific components perform on this emerging class of mobile devices. Although we have not done exhaustive testing, and although these browsers are revving quickly and present a moving target, our goal is to provide some early, provisional advice to help you get started as you contemplate how your YUI-based application will render in the mobile world.
More Information:
- Challenges of Interface Design for Mobile Devices - YUI Blog article by Lucas Pettinati, Yahoo! Sr. Interaction Designer.
- Performance Research, Part 5: iPhone Cacheability - Making it Stick - YUI Blog article by Tenni Theurer and Wayne Shea from the Yahoo! Exceptional Performance Team
Support & Community
The YUI Library and related topics are discussed on the on the YUILibrary.com forums.
Also be sure to check out YUIBlog for updates and articles about the YUI Library written by the library's developers.
Filing Bugs & Feature Requests
The YUI Library's public bug tracking and feature request repositories are located on the YUILibrary.com site. Before filing new feature requests or bug reports, please review our reporting guidelines.
Carousel Control Examples:
- Spotlight example
- Circular Carousel example
- Partially revealing previous and next items
- Using both images and text within an item
- Using Ajax for deferred loading of items
- Using deferred loading of items and Carousel's built-in paginator
- Multi-row example
- Pagination template example
- Using Paginator with Carousel
- Using the Carousel ARIA Plugin
YUI Carousel Control on del.icio.us:
All YUI 2.x users should review the YUI 2.8.2 security bulletin, which discusses a vulnerability present in YUI 2.4.0-2.8.1.
- YUI Library
- YUI Home
- YUI 3
- YUIBlog
- Bug Reports/Feature Requests
- YUI on GitHub
- YUI License
- YUI 2.x Resources
- YUI 2 Archives
- YUI 2 Examples
- YUI 2 API Docs
- YUI 2 Discussion Forums
- YUI Components
- Animation
- AutoComplete
- Browser History Manager
- Button
- Calendar
- Carousel
- Charts
- Color Picker
- Connection Manager
- Container
- Cookie
- DataSource
- DataTable
- Dom
- Drag & Drop
- Element
- Event
- Get
- ImageCropper
- ImageLoader
- JSON
- Layout Manager
- Logger
- Menu
- Paginator
- Profiler
- ProfilerViewer
- ProgressBar
- Resize
- Rich Text Editor
- Selector
- Slider
- Storage
- StyleSheet
- SWF
- SWFStore
- TabView
- TreeView
- Uploader
- Yahoo Global Object
- YUI Loader
- YUI Test
- Reset CSS
- Base CSS
- Fonts CSS
- Grids CSS
Copyright © 2013 Yahoo! Inc. All rights reserved.