YUI 2: AutoComplete
YUI 2: AutoComplete
 The AutoComplete control provides the front-end logic for text-entry suggestion and completion functionality. See the Yahoo! UI Design Pattern Library description for AutoComplete to get a fuller sense of the underlying design patterns in the AutoComplete family. AutoComplete provides a high degree of configurability so developers can implement these design patterns quickly and flexibly. Top features include custom formatting, query delimiters, animation, custom formatting, a rich Custom Event model, and much more.
The AutoComplete control provides the front-end logic for text-entry suggestion and completion functionality. See the Yahoo! UI Design Pattern Library description for AutoComplete to get a fuller sense of the underlying design patterns in the AutoComplete family. AutoComplete provides a high degree of configurability so developers can implement these design patterns quickly and flexibly. Top features include custom formatting, query delimiters, animation, custom formatting, a rich Custom Event model, and much more.
Note: As of the 2.6.0 release, AutoComplete has been migrated to use YAHOO.util.DataSource, which is now a new required dependency. The YAHOO.widget.DataSource class, which used to be packaged with the AutoComplete Control has been removed. While backward compatibility has been maintained whenever possible, implementers who are upgrading from an earlier version are strongly advised to read the Upgrade Notes to smooth the transition.
On This Page:
- Upgrade Notes
- Getting Started
- Instantiating AutoComplete
- Customizing the DataSource Request Syntax
- Common Configurations
- Custom Formatting of Results
- Security Considerations
- Data Matching Algorithms
- Custom Events and "doBefore" Abstract Methods
- Skinning AutoComplete
- AutoComplete Storyboard Matrix
- Known Issues
- YUI on Mobile Devices
- Support & Community
- Filing Bugs and Feature Requests
Quick Links:
- Examples: Explore examples of the AutoComplete Control in action.
- API Documentation: View the full API documentation for the AutoComplete Control.
- Release Notes: Detailed change log for the AutoComplete Control.
- License: The YUI Library is issued under a BSD license.
- Download: Download the AutoComplete Control as part of the full YUI Library at YUILibrary.com.
Upgrade Notes
Users new to AutoComplete can skip this section and proceed directly to the Getting Started section. Implementers who are upgrading from previous versions should note that as of version 2.6.0, AutoComplete has been migrated from YAHOO.widget.DataSource to YAHOO.util.DataSource, which is now a new external dependency. Implementers are strongly advised to review the DataSource utility and update their implementations at their earliest convenience. The following important changes to AutoComplete should also be noted:
- Implementers may now need to define an explicit width in CSS on the AutoComplete wrapper element that contains the input and container elements.
- The YAHOO.widget.DataSource properties
queryMatchCase,queryMatchContains, andqueryMatchSubsethave been ported over to be YAHOO.widget.AutoComplete properties of the same name, and are now handled directly within AutoComplete code. - The YAHOO.widget.DS_XHR properties
scriptQueryParamandscriptQueryAppendhave been deprecated in favor of the new customizeable YAHOO.widget.AutoComplete methodgenerateRequest(). - The YAHOO.widget.DS_XHR property
responseStripAfterhas been deprecated in favor of the new customizeable YAHOO.util.DataSource abstract methoddoBeforeParseData. - Requests sent to XHR DataSources can now be configured not to insert the "?" in the query string by setting the
queryQuestionMarkproperty tofalse. To more fully customize the query syntax, implementers should override the new generateRequest() method. - As a convenience, the formatResult() method now recieves a third parameter which is the query matching string for the result.
- The result object used within AutoComplete, which is one of the values passed to the
formatResult()method supports either a backwards-compatible array structure or a more performant and robust object literal structure. The object literal structure is enabled by setting theresultTypeListproperty tofalse.
Getting Started
To use the AutoComplete control, include the following source files in your web page with the script tag:
<!--CSS file (default YUI Sam Skin) --> <link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/autocomplete/assets/skins/sam/autocomplete.css"> <!-- Dependencies --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/yahoo-dom-event/yahoo-dom-event.js"></script> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/datasource/datasource-min.js"></script> <!-- OPTIONAL: Get (required only if using ScriptNodeDataSource) --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/get/get-min.js"></script> <!-- OPTIONAL: Connection (required only if using XHRDataSource) --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/connection/connection-min.js"></script> <!-- OPTIONAL: Animation (required only if enabling animation) --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/animation/animation-min.js"></script> <!-- OPTIONAL: JSON (enables JSON validation) --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/json/json-min.js"></script> <!-- Source file --> <script src="http://yui.yahooapis.com/2.9.0/build/autocomplete/autocomplete-min.js"></script>
yui-skin-sam class name to an element that is a parent of the element
in which the AutoComplete Control lives. You can usually accomplish this simply by putting the class on the
<body> tag:
<body class="yui-skin-sam">
For more information on skinning YUI components and making use of default skins, see our Understanding YUI Skins article here on the website.
YUI Dependency Configurator:
Instead of copying and pasting the filepaths above, try letting the YUI dependency Configurator determine the optimal file list for your desired components; the Configurator uses YUI Loader to write out the full HTML for including the precise files you need for your implementation.
Note: If you wish to include this component via the YUI Loader, its module name is autocomplete. (Click here for the full list of module names for YUI Loader.)
Where these files come from: The files included using the text above will be served from Yahoo! servers. JavaScript files are minified, meaning that comments and white space have been removed to make them more efficient to download. To use the full, commented versions or the -debug versions of YUI JavaScript files, please download the library distribution and host the files on your own server.
Order matters: As is the case generally with JavaScript and CSS, order matters; these files should be included in the order specified above. If you include files in the wrong order, errors may result.
Instantiating AutoComplete
Your AutoComplete implementation will consist of two objects:
- A DataSource instance. A DataSource manages the query-response cycle of data retrieval from a variety of sources, from local JavaScript arrays to remote online servers. Please refer to the DataSource documentation for more information on using this utility. Note that when using a LocalDataSource, the first item defined in the LocalDataSource schema's fields array points to the data values against which queries are matched.
- An AutoComplete instance. AutoComplete queries the DataSource and presents the result data back to the user.
The following code implements AutoComplete on your page:
// An outer container contains an input element and // a empty results container, both of which are passed // to the constructor <div id="myAutoComplete"> <input id="myInput" type="text"> <div id="myContainer"></div> </div>
var myAutoComp = new YAHOO.widget.AutoComplete("myInput","myContainer", myDataSource);
The AutoComplete constructor has three required parameters:
- the ID string or element reference to the input field (a textbox or textarea) where users will type queries
- the ID string or element reference to the HTML container in which the query results will be displayed
- a DataSource instance
Customizing the DataSource Request Syntax
AutoComplete sends the user-typed query value directly to the DataSource for results. By default, requests sent to XHR DataSources are prepended with a "?" and the parameter name "query":
// XHR request string sent to the DataSource "?query={query}";
As of version 2.6.0, AutoComplete can be configured not to insert the "?" in the query string by setting the queryQuestionMark property to false:
// queryQuestionMark is set to false "query={query}";
Implementers can entirely modify these requests by redefining the generateRequest() method, which is especially important for remote server requests that need to have a specific syntax.
myAutoComp.generateRequest = function(sQuery) { return "/search/" + sQuery + "/other/data"; };
Common Configurations
The AutoComplete class provides many configuration parameters that allow you to fine-tune the user experience of your AutoComplete instance, including:
- Animation
- Delimiter Characters
- Maximum Results Displayed
- Minimum Query Length
- Query Delay
- Auto-highlight
- Highlight Class Name
- Pre-highlight Class Name
- Use Shadow
- Use iFrame
- Force Selection
- Type Ahead
- Allow Browser Autocomplete
- Always Show Container
Animation
If you include the YUI Animation utility on your web page, you can enable animation on the transitions of the AutoComplete container element using the following code:
// Container will expand and collapse vertically myAutoComp.animVert = true; // Container will expand and collapse horizontally myAutoComp.animHoriz = true; // Container animation will take 2 seconds to complete myAutoComp.animSpeed = 2;
By default, if the Animation utility is present, the container will animate vertically, but not horizontally, over 0.3 seconds.
Delimiter Characters
By default, AutoComplete treats the user's input as a single string. Use the delimChar parameter to accept multiple delimited queries. Think about the way commas or semicolons are used to separate email addresses in an email application: enabling AutoComplete query delimiters is an easy way to help users address an email to multiple recipients in a single input box. By using delimChar to define an array of single characters, you may define more than one character that will delimit user queries. However, queries are not supported for when users are typing between existing delimited strings -- only the string after the last delimiter will be queried. Note: We do not recommend defining delimiter characters when the force selection feature (see below) is enabled, or vice versa.
// Semi-colons may delimited queries... myAutoComp.delimChar = ";"; // ...or commas and/or spaces may delimited queries... myAutoComp.delimChar = [","," "]; // ...or disable query delimiters altogether (default) myAutoComp.delimChar = "";
Maximum Results Displayed
When query results return, an HTML unordered list element (<ul>) of up to ten items (<li> elements) are rendered into the container that you specify. If fewer than ten results are returned, the container's <ul> element will only have that number of <li> elements. Keep in mind that the height, width, and other style characteristics of the container are determined by CSS. You may use the following code to change the maximum number of <li> elements that may populate the <ul> element:
// Display up to 20 results in the container myAutoComp.maxResultsDisplayed = 20;
Minimum Query Length
By default, as soon as a user starts typing characters into the input element, the AutoComplete control starts batching characters for a query to the DataSource. You may increase how many characters the user must type before triggering this batching, which can help reduce load on a server, especially if the first few characters of the input string will not produce meaningful query results. A value of 0 will enable null or empty string queries, which is particularly useful in conjunction with the Always Show Container feature. A negative number value will effectively turn off the widget.
// Require user to type at least 3 characters before triggering a query myAutoComp.minQueryLength = 3;
Query Delay
By default, AutoComplete batches user input and sends queries 0.1 seconds from the last key input event. You may adjust this delay for optimum user experience and/or server load. Keep in mind that this value only reflects the delay before sending queries, and any delays in receiving query results that may be caused by server or computational latency will not be reflected in this value. This value must be a Number greater than 0.
// Key input events will trigger queries ASAP... myAutoComp.queryDelay = 0.1; // ...or queries will be sent after 3 seconds have passed // since the last key input event myAutoComp.queryDelay = 3;
Auto-highlight
By default, when the container populates with query results, the first item in the list will be automatically highlighted for the user. Use the following code to disable this feature:
// Do not automatically highlight the first result item in the container myAutoComp.autoHighlight = false;
Highlight Class Name
By default, each <li> element of the container's <ul> element is assigned the class name yui-ac-highlight when it is selected. Style sheet examples have been provided for you in the AutoComplete examples . To customize the CSS of these elements, be sure to define a custom class and set the following configuration parameter:
// Use a custom class for LI elements myAutoComp.highlightClassName = "myCustomHighlightClass";
Pre-highlight Class Name
If you would like to have user mouseover events on results list items trigger a different visual cue than arrow-key events, be sure to define a custom prehighlight class and set the following configuration parameter:
// Use a custom class for mouseover events myAutoComp.prehighlightClassName = "myCustomPrehighlightClass";
Use Shadow
If you would like the container element to have a drop-shadow, be sure to define a class yui-ac-shadow and enable the feature with the following code:
// Enable a drop-shadow under the container element myAutoComp.useShadow = true;
Use iFrame
An iFrame under the container element is meant to work around a known IE6 bug that causes form select elements to be displayed over elements with a higher z-index. If you would like the container element to have an iFrame shim, be sure to enable the feature for IE5.x and IE6 users with the following code:
// Enable an iFrame shim under the container element myAutoComp.useIFrame = true;
Force Selection
You can enable the force-selection feature to require your users to select a result from the container, or else the input field is cleared of whatever they have typed. If the user types a string that does not match any query result, the input will be deleted from the field. Note: We do not recommend enabling the force-selection feature when delimChar is defined, or vice versa.
// Enable force selection myAutoComp.forceSelection = true;
Type Ahead
Enabling the type-ahead feature causes the user's input to be automatically completed with the first query result in the container list. The string in the input field is also pre-selected, so it can be deleted as the user continues typing.
// Enable type ahead myAutoComp.typeAhead = true;
Allow Browser Autocomplete
Some browsers support a non-standard attribute on form elements called "autocomplete". When "autocomplete" is set to "on", the browser provides a built-in automatic completion mechanism — and it will cache the user input for automatic display if the user uses the "Back" button to navigate back to the page. In order for the YUI AutoComplete control to perform properly, the built-in browser completion mechanism needs to be suppressed. Therefore, the control sets the autocomplete attribute to "off" when the user starts typing in in an AutoComplete input field. However, the control will set the autocomplete attribute back to "on" if the form is submitted, so that a user's input can be displayed, should the "Back" button get clicked after form submission. This caching of user input may not be desired for sensitive data such as credit card numbers. Where you are dealing with sensitive user data, you should disable this feature with the following code:
// Disable the browser's built-in autocomplete caching mechanism myAutoComp.allowBrowserAutocomplete = false;
Always Show Container
By default, the AutoComplete control shows the container when it is populated with query results and then hides it when the user interaction is complete. Enabling alwaysShowContainer prevents the container from toggling to a collapsed state when the user is done interacting with the widget.
// Always show the container element myAutoComp.alwaysShowContainer = true;
Custom Formatting of Results
When query results are returned by the DataSource instance to the AutoComplete instance, the data is fed, one result at a time, into an AutoComplete instance method called formatResult. Many AutoComplete implementers override this method directly in their AutoComplete instance to achieve custom formatting. If you do this, start with the default formatResult method code to get started and make whatever changes you need.
The formatResult() function processes one query result at a time and returns HTML markup to display for that result. Alternatively, the formatEscapedResult() function HTML-escapes the result strings before displaying to the user. The first argument to these methods is the data for the result (as defined by the DataSource responseSchema.fields property). The original user-typed query string as the second argument, and the specific matching field is passed in as the third argument. As of version 2.6.0, the result data can be passed in either as an array or an object literal, depending on the value of the resultTypeList property. For performance and robustness, the object literal mode is recommended:
// This is the default formatResult function myAutoComplete.formatResult = function(oResultData, sQuery, sResultMatch) { var sMarkup = (sResultMatch) ? sResultMatch : ""; return sMarkup; }; // This is the alternative formatEscapedResult function myAutoComplete.formatEscapedResult = function(oResultData, sQuery, sResultMatch) { var sResult = (sResultMatch) ? sResultMatch : ""; return YAHOO.lang.escapeHTML(sResult); }; // Enable HTML-escaping of result strings myAutoComplete.formatResult = myAutoComplete.formatEscapedResult; // Result as object literal (recommended) myDataSource.responseSchema = {fields: ["name", "moreData"]}; myAutoComplete.resultTypeList = false; myAutoComplete.formatResult = function(oResultData, sQuery, sResultMatch) { return (sResultMatch + " (" + oResultData.moreData + ")"); }; // Result as array (backward compatible) myAutoComplete.formatResult = function(oResultItem, sQuery, sResultMatch) { var sKey = sResultMatch; var oAdditionalData = oResultItem[1]; return (sKey + " (" + oAdditionalData.moreData + ")"); };
Here's an example of a customized formatResult method that bolds the original query term and additionally displays two supplemental data points:
// This function returns markup that bolds the original query, // and also displays to additional pieces of supplemental data. myAutoComp.resultTypeList = false; myAutoComp.formatResult = function(oResultData, sQuery, sResultMatch) { var sKey = sResultMatch // Extract the part of the match that the user did not type var sKeyRemainder = sKey.substr(sQuery.length); // some other piece of data defined by schema var moreData1 = oResultData.moreData1; // and another piece of data defined by schema var moreData2 = oResultData.moreData2; var aMarkup = ["<div class='myCustomResult'>", "<span style='font-weight:bold'>", sKey, "</span>", sKeyRemainder, ": ", moreData1, ", ", moreData2, "</div>"]; return (aMarkup.join("")); };
Security Considerations
When working with data from third-party sources, user input data, or otherwise untrustworthy sources, implementers need to be aware that these values may be inserted into the DOM by AutoComplete. If you are working with questionable data, you may point to the formatEscapedResult() method available in version 2.9.0, which will HTML-escape all string data before insertion into the DOM:
// Point to the formatter that will HTML-escape your data myAutoComplete.formatResult = myAutoComplete.formatEscapedResult;
Implementers who are overriding the formatResult() method should be sure to escape the data in their custom function as necessary. The YAHOO.lang.escapeHTML() method is available in version 2.9.0 for your convenience.
Data Matching Algorithms
Setting the applyLocalFilter property to true enables client-side data-matching on your result data via the overridable filterResults() method. Using a LocalDataSource automatically sets the applyLocalFilter property to be true, but otherwise you should be sure to set it explicitly. By default, filterResults() will match queries against result data values defined by the first item in the DataSource schema's fields array. Additionally, there are several built-in properties that can also be enabled in conjunction with applyLocalFilter:
The queryMatchCase property enables case-sensitivity in the such that only case-sensitive matches will return.
// Match case sensitivity myAutoComplete.applyLocalFilter = true; myAutoComplete.queryMatchCase = true;
The queryMatchContains property searches for results that "contain" the query string at any position, rather than only at the start.
// Match results that *contain* the query string as well as results that start with query string myAutoComplete.applyLocalFilter = true; myAutoComplete.queryMatchContains = true;
Subset matching can play an important role in achieving a robust and performant cache experience. When DataSource caching is enabled, AutoComplete queries for "foo" can get cached with 100 results. If queryMatchSubset is enabled, any query thereafter that starts with "foo" (e.g., "food" or "fool") goes first to the DataSource cache and retrieves results that are a subset of the 100 results that got cached for "foo". With subset caching off, "foo" and "food" are cached separately and treated as independent entries. If your data universe is enormous (as is often the case in Yahoo! applications), you probably want to return the best 100 matches for "foo" and the best 100 matches for "food" separately. On much smaller datasets where the cached results for "foo" will reliably contain the superset of matches for the query "food", subset caching can reduce trips to the live data source and help improve performance. Note that even with subset caching enabled, if the cache returns no valid results, a query will be made to the live data source.
// Match results of query strings that are cached *subsets* of the current query string myDataSource.maxCacheEntries = 100; myAutoComplete.queryMatchSubset = true;
Custom Events and "doBefore" Abstract Methods
AutoComplete offers a robust set interesting moments via a set of Custom Events to which you can subscribe and "doBefore" abstract methods which you can implement. The syntax for subscribing to AutoComplete events is simple; here's an example using itemSelectEvent, which gets passed an array argument (aArgs) containing the following members:
- AutoComplete instance: a reference to the AutoComplete instance that is firing the event;
- Element: a reference to the DOM list item element (LI) that has been selected in the container;
- Data: an object literal containing the data for the selected item, as defined by the DataSource
responseSchema.
//define your itemSelect handler function: var itemSelectHandler = function(sType, aArgs) { YAHOO.log(sType); // this is a string representing the event; // e.g., "itemSelectEvent" var oMyAcInstance = aArgs[0]; // your AutoComplete instance var elListItem = aArgs[1]; // the <li> element selected in the suggestion // container var oData = aArgs[2]; // object literal of data for the result }; //subscribe your handler to the event, assuming //you have an AutoComplete instance myAC: myAC.itemSelectEvent.subscribe(itemSelectHandler);
For a full list of AutoComplete events, see the event list in the AutoComplete API documentation.
The doBeforeLoadData() method gives implementers access to the DataSource response before it is consumed by the AutoComplete instance and rendered into the results container.
The doBeforeExpandContainer() method gives implementers access to result data and DOM elements after the container has been rendered with results but before it is displayed to the user, for example to move the container to a different position on the screen.
Skinning AutoComplete
AutoComplete comes with a default presentation or "skin," part of the "Sam Skin" visual treatment that accompanies most YUI controls. You can read more about the general approach to skinning YUI components in this in-depth article.
The CSS provided with AutoComplete is comprised of core, functional CSS as well as the Sam Skin visual treatment.

To explore the CSS which controls the AutoComplete's presentation, please review the AutoComplete Skinning Example wherein the full CSS for the control is displayed.
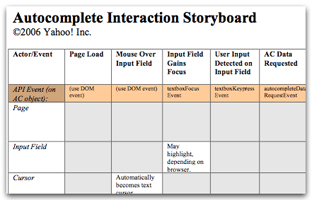
AutoComplete Storyboard Matrix
Storyboarding can be a powerful strategy for thinking through a rich interaction during the design phase. We have created a storyboard matrix for AutoComplete (also available as a .doc file) that helps you track the actors and the events that are important when a AutoComplete interaction is taking place. Interesting moments (which correspond to the API events to which you can subscribe handlers) are listed across the top; each row in the matrix represents an element. Consider printing out the matrix and using it in planning sessions between interaction architects and engineers as you think through the nuances of your implementation.
Top Known Issues
Please see the bug repository at YUILibrary.com for a complete list of known issues.
Custom CSS Required for Vertically Stacking Multiple AutoCompletes
Vertically stacked AutoComplete instances need custom CSS for IE<8. Please see the example here for the details of a workaround: http://developer.yahoo.com/yui/examples/autocomplete/ac_combobox.html
Bleed-through Scrollbars on Mac Firefox
Due to a known bug, the AutoComplete suggestion container may display underlying scrollbars.
YUI on Mobile: Using AutoComplete Control with "A-Grade" Mobile Browsers
About this Section: YUI generally works well with mobile browsers that are based on A-Grade browser foundations. For example, Nokia's N-series phones, including the N95, use a browser based on Webkit — the same foundation shared by Apple's Safari browser, which is found on the iPhone. The fundamental challenges in developing for this emerging class of full, A-Grade-derived browsers on handheld devices are:
- Screen size: You have a much smaller canvas;
- Input devices: Mobile devices generally do not have mouse input, and therefore are missing some or all mouse events (like mouseover);
- Processor power: Mobile devices have slower processors that can more easily be saturated by JavaScript and DOM interactions — and processor usage affects things like battery life in ways that don't have analogues in desktop browsers;
- Latency: Most mobile devices have a much higher latency on the network than do terrestrially networked PCs; this can make pages with many script, css or other types of external files load much more slowly.
There are other considerations, many of them device/browser specific (for example, current versions of the iPhone's Safari browser do not support Flash). The goal of these sections on YUI User's Guides is to provide you some preliminary insights about how specific components perform on this emerging class of mobile devices. Although we have not done exhaustive testing, and although these browsers are revving quickly and present a moving target, our goal is to provide some early, provisional advice to help you get started as you contemplate how your YUI-based application will render in the mobile world.
More Information:
- Challenges of Interface Design for Mobile Devices - YUI Blog article by Lucas Pettinati, Yahoo! Sr. Interaction Designer.
- Performance Research, Part 5: iPhone Cacheability - Making it Stick - YUI Blog article by Tenni Theurer and Wayne Shea from the Yahoo! Exceptional Performance Team
We've tested the AutoComplete Control on several high-end smart phones with varying degrees of success. Due to high network latency, limited real estate, and inconsistent user interface models, the AutoComplete Control is not recommended as a good fit for these devices at this time.
Of the devices we've tested, the iPhone shows the most potential, and the following points are meant to give preliminary and cautionary guidance for developers implementing solely for that platform:
- At this time, there is no known workaround to disable the native browser
autocompleteattribute. Therefore, the native suggestion box may be redundantly displayed during user interactions with the AutoComplete control. - The
typeAheadfeature is not supported. - High latency use cases are not recommended.
- Designs should take into careful consideration the very limited screen real estate caused by the keyboard display. Before you implement, be sure to test this yourself on an iPhone or iPod Touch. While AutoComplete works on those devices, the keyboard placement and pagezoom hide the suggestion container almost completely.
Support & Community
The YUI Library and related topics are discussed on the on the YUILibrary.com forums.
Also be sure to check out YUIBlog for updates and articles about the YUI Library written by the library's developers.
Filing Bugs & Feature Requests
The YUI Library's public bug tracking and feature request repositories are located on the YUILibrary.com site. Before filing new feature requests or bug reports, please review our reporting guidelines.
AutoComplete Control Examples:
- Basic Local Data
- Basic Remote Data
- Screenreader Accessibility
- Customizing Remote Requests
- Custom Formatting, with a Proxyless Remote DataSource
- Searching Field A, Submitting Field B with itemSelectEvent
- Combobox, with CSS for Multiple Stacked Instances
- Tagging Example with alwaysShowContainer
- FunctionDataSource to Search Multiple Fields of an Address Book at Runtime
- Centering AutoComplete On a Page
- Subset Matching
- Find Photos on Flickr
- Configurations Dashboard
- Skinning Model
Other YUI Examples That Make Use of the AutoComplete Control:
- Flickr Image Search (included with examples for the Rich Text Editor)
- Logger Integration with YUI Components (included with examples for the Logger Control)
- Datatable with Autocomplete (included with examples for the DataTable Control)
- Complex Application (included with examples for the Layout Manager)
More Reading about the YUI AutoComplete Control:
- Implementing Search Suggest with YUI and the Yahoo Search API, by Eric Miraglia on InsideRIA
- Using YUI AutoComplete within a Dialog, by the YUI Team
- YUI Autocomplete AJAX Select Drowdown with ID, by James Gardner
- Video of an YUI AutoComplete conference presentation by YUI engineer Eric Miraglia at Real-World Ajax, April 2006
YUI AutoComplete on del.icio.us:
All YUI 2.x users should review the YUI 2.8.2 security bulletin, which discusses a vulnerability present in YUI 2.4.0-2.8.1.
- YUI Library
- YUI Home
- YUI 3
- YUIBlog
- Bug Reports/Feature Requests
- YUI on GitHub
- YUI License
- YUI 2.x Resources
- YUI 2 Archives
- YUI 2 Examples
- YUI 2 API Docs
- YUI 2 Discussion Forums
- YUI Components
- Animation
- AutoComplete
- Browser History Manager
- Button
- Calendar
- Carousel
- Charts
- Color Picker
- Connection Manager
- Container
- Cookie
- DataSource
- DataTable
- Dom
- Drag & Drop
- Element
- Event
- Get
- ImageCropper
- ImageLoader
- JSON
- Layout Manager
- Logger
- Menu
- Paginator
- Profiler
- ProfilerViewer
- ProgressBar
- Resize
- Rich Text Editor
- Selector
- Slider
- Storage
- StyleSheet
- SWF
- SWFStore
- TabView
- TreeView
- Uploader
- Yahoo Global Object
- YUI Loader
- YUI Test
- Reset CSS
- Base CSS
- Fonts CSS
- Grids CSS
Copyright © 2013 Yahoo! Inc. All rights reserved.